Reacting Flows & Combustion
CFD Simulation of Reacting Flows and Combustion: Engine & Gas Turbine, Fuel Injector & Spray, Exhaust Aftertreatment with Detailed Chemistry
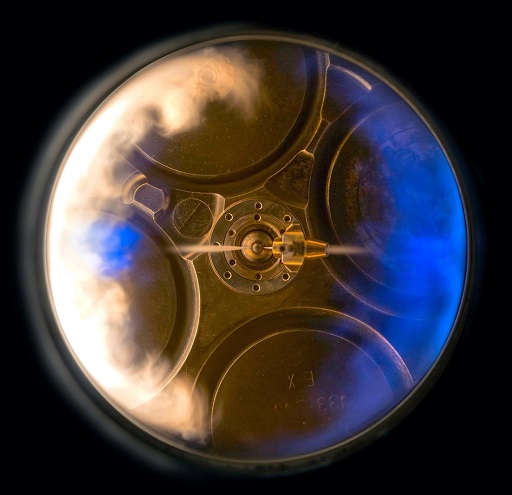
Combustion is a complex process that involves the interaction of fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and chemical kinetics. In order to design efficient combustion systems, it is important to understand the underlying physics and chemistry of the process. Reacting flows and combustion simulations can be used to model and predict the behavior of combustion systems under different conditions.
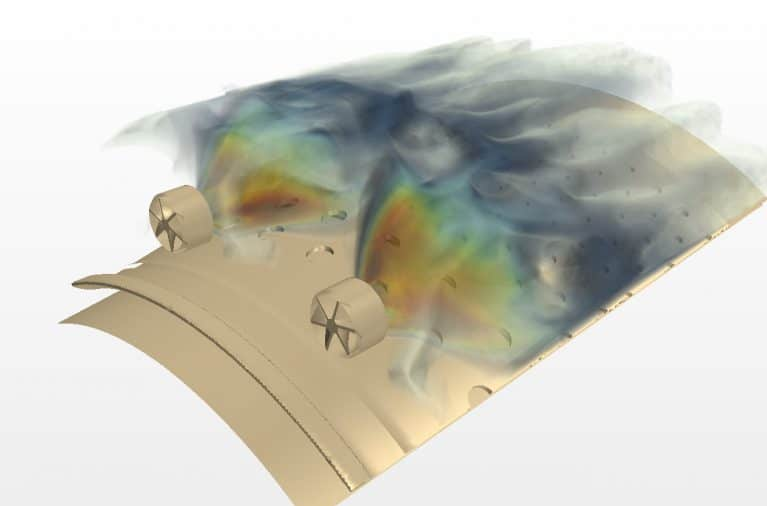
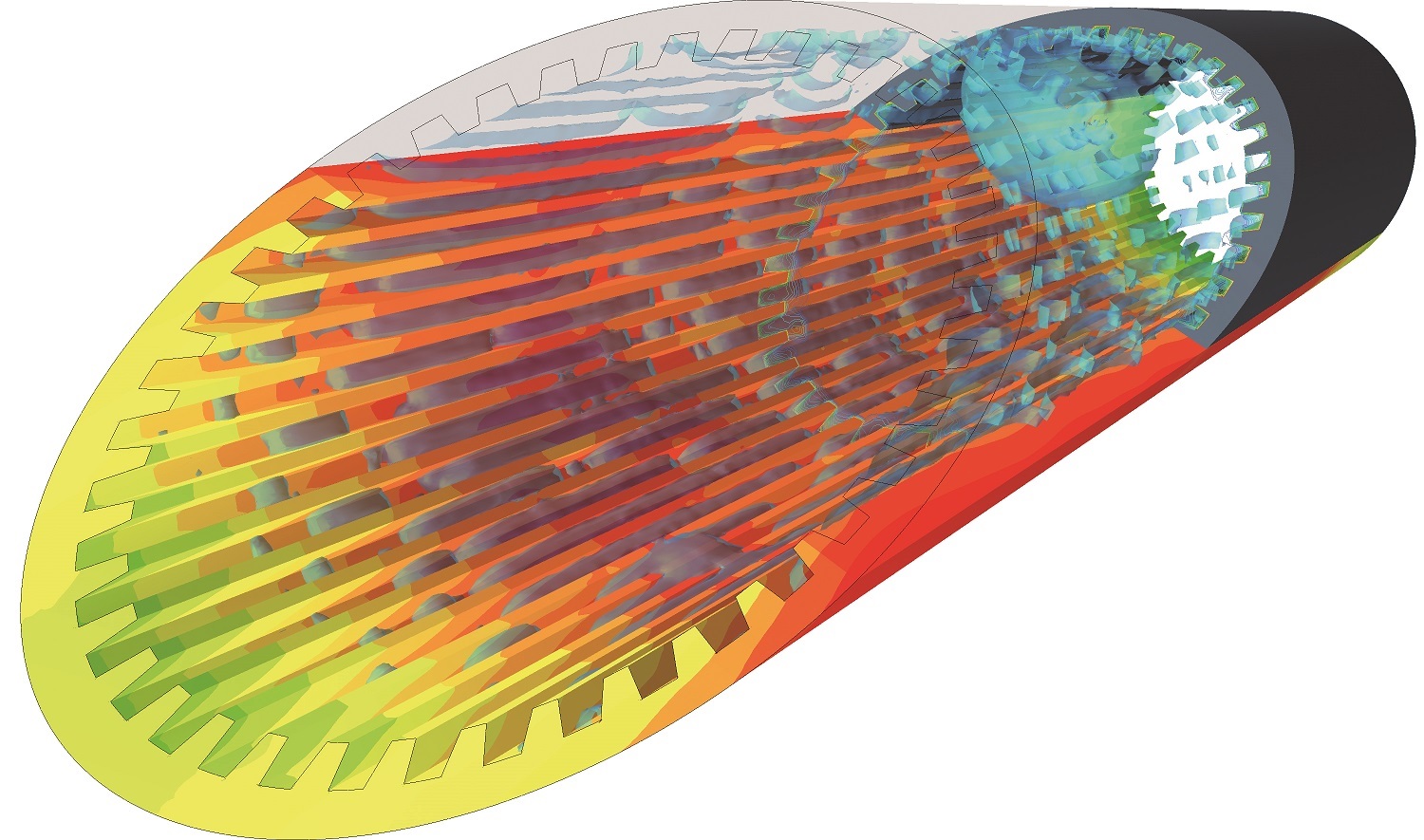
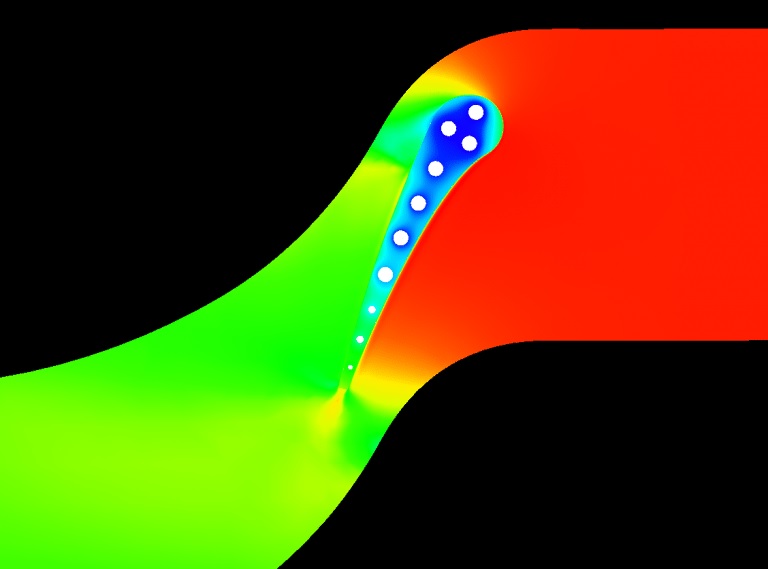
Reacting flows refer to fluid flows that involve chemical reactions. Combustion is a typical example of a reacting flow, where fuel and oxidizer are mixed together and ignite to release heat energy. Combustion simulations involve solving the governing equations of fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and chemical kinetics, along with boundary conditions and initial conditions, to predict the behavior of the combustion system.
The accurate modeling of combustion chemistry is critical to designing efficient and environmentally friendly combustion systems. Chemical kinetics models describe the chemical reactions that take place during combustion, including the rate at which reactants are consumed and products are formed. Advanced chemistry solvers, such as detailed chemical kinetic mechanisms or reduced chemical models, can be used to predict the formation of pollutants and other undesirable combustion byproducts.